- Getting ESOP as salary package? Know about ESOP Taxation
- Frequently asked questions about stock options and tax implications
- Non-Qualified Stock Options
- How stock options work
It could easily become a nightmare if you've never dealt with stock options before. Here are a few insights to take the confusion away so you can maximize the potential of this incredible work benefit. There are two main types of stock options that you could receive as part of your compensation gift: incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options.
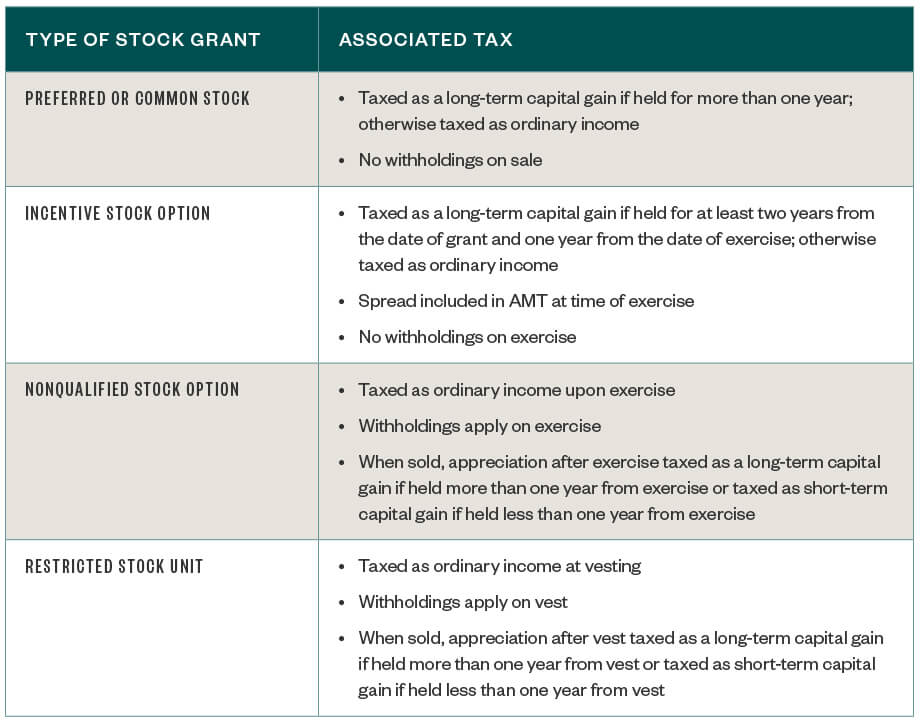
The main difference between these two is how they are treated for tax purposes when you exercise the options. Incentive stock options ISOs , also known as statutory stock options, are granted under a stock purchase plan.
- forex hard!
- strategy trading binary;
- forex risk management spreadsheet;
However, nonqualified stock options NSOs are granted without a specific type of plan and are often referred to as nonstatutory stock options. When you have employee stock options, there are three special occasions you need to be aware of: the date your company granted you the options, when you exercised them, and how long you hold the shares you receive on exercise before you sell them.
These moments play an important role in your tax calculation. Most of the time, there is a vesting schedule tied to your employee stock options. Simply put, you cannot tap into your stock option benefits until you've been at your company for a certain period of time. After you are vested, then you can exercise the options at any time before they expire.
Incentive stock options are simpler than nonqualified stock options from a tax perspective. Employees who have ISOs don't have to worry about taxes when they receive a stock option grant or exercise the options. The order of operations works like this: You receive a stock option grant and then you exercise the options when you are eligible and ready to do so. After you exercise your options, then you'll have to make the ultimate decision: When do I sell my stock? Your other option: exercise your options in one period and sell your stocks later.
Getting ESOP as salary package? Know about ESOP Taxation
It's important to have a tax strategy when exercising NSOs because you'll be hit with a tax twice, and it can get a bit complicated. First, you'll typically have to pay ordinary income taxes when you exercise the options. You must pay the difference between what you paid for the stock the exercise price and the fair value of the shares when you exercised them. The IRS considers this as compensation income even though you haven't actually made any money.
Then, you'll pay capital gains tax if you sell the shares at a profit.
Frequently asked questions about stock options and tax implications
If the sale results in a loss, you'll report a capital loss for the difference between your tax basis and what you received. You'll either pay short-term or long-term capital gains taxes depending on how long you've held the stock. Taxes for employee stock options can be overwhelming. If you have no idea what you're doing when you file your taxes , seek out a professional to make the process less draining.
Investing This process isn't completely straightforward so please check out this page for more on how to claim AMT Credits. A solution for reducing this risk is to obtain an advance from the Employee Stock Option Fund to cover the entire cost of exercising your stock options, including the tax. For more information on tax savings , please contact us at the Employee Stock Option Fund.
This innovative service promotes and enables a healthier relationship between companies and employees. I my opinion it's valuable to employees and great for the overall tech environment and economy. It is good for nobody when employees feel trapped because they can't afford to leave. In less extreme cases exercising can be expensive and somewhat risky and this is simply a good smart hedge and a good square deal. How are Stock Options Taxed? How are employee stock options taxed? The post will cover how stock option taxation works at two points in time: 1.
Upon Exercise 2. Your options are taxed differently upon exercise depending on what type of options you own, however the way taxes are calculated and the cost of exercising remains the same: Type of Equity Vesting Exercise Sale ISOs or "Incentive Stock Options" No Taxes! RSUs unlike options do not need to be exercised. Ordinary income tax rate.
Non-Qualified Stock Options
Get in touch We'll get back to you as soon as possible. Thank you! Your submission has been received! A deal manager will contact you as soon as possible. All Rights Reserved.
How stock options work
The ESO Fund does not provide legal, financial, or tax advice. About Terms of Service Privacy Policy. RSUs are taxed upon vesting unless they have a "double trigger" vesting schedule.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Get_the_Most_Out_of_Employee_Stock_Options_Oct_2020-01-e28cc3504d694dcaaa7a45dfed666f0b.jpg)