- Part 3: Exercising stock options and taxes
- Tax advantaged share plans—UK and US comparison
- Equity How stock options are taxed | Carta
- Comparison of UK and US share incentive arrangements
This resource is continually monitored and revised for any necessary changes due to legal, market, or practice developments. Any significant developments affecting this resource will be described below. What's on Practical Law? Show less Show more.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Get_the_Most_Out_of_Employee_Stock_Options_Oct_2020-02-e2a3aeb7d91347578e72df8195d0e8f0.jpg)
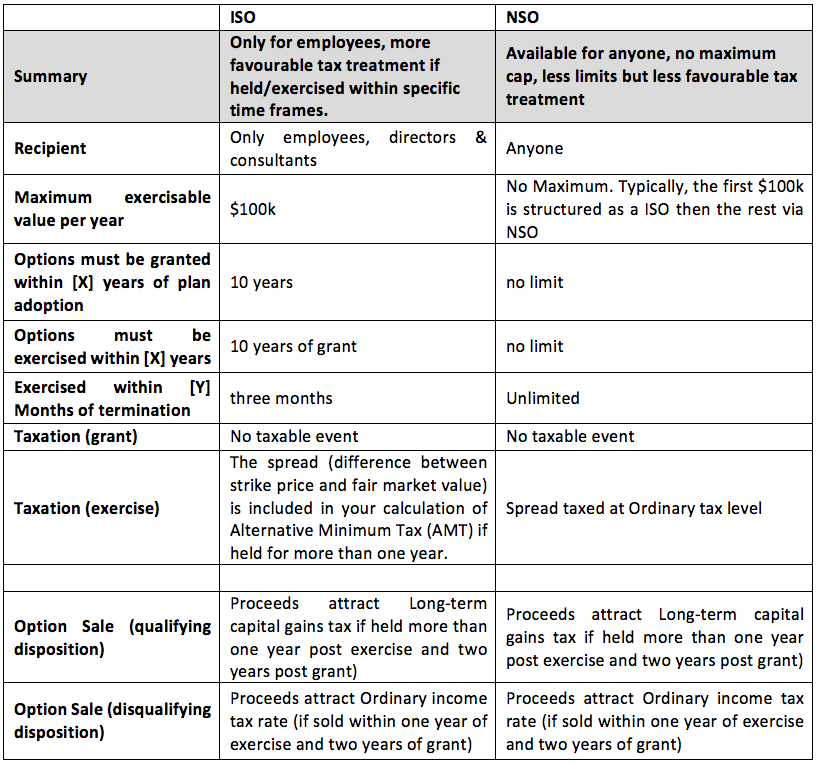
Ask a question. Related Content. A Checklist outlining the requirements that must be satisfied for a stock option to qualify as an incentive stock option ISO under Section of the Internal Revenue Code and receive more favorable employee tax treatment than non-qualified stock options. An individual who exercises a non-qualified stock option must pay ordinary income taxes on the excess of the fair market value of the underlying shares on exercise over the exercise price the "spread".
Part 3: Exercising stock options and taxes
However, ISOs are not subject to ordinary income taxes if the shares are held for both:. For the reason indicated in 3 above, this will not work for US purposes and options issued to US employees will need to have a US-qualifying fair market value exercise price. Consequently, you need to address up-front whether you are going to have different exercise prices in simultaneous grants of options to your UK and US employees and, if so, whether this should have any impact on grant levels.
Differences in market practice may affect the determination of fair market value of employee grants. One way in which US issuers can justify a lower fair market value for their common stock ordinary shares or common stock options issued to employees is that outside investors in those issuers instead receive convertible preferred stock convertible preference shares with a liquidation preference. This liquidation preference provides, at a minimum, a right to get paid first in certain circumstances before the common stock receives any value.
As a result, a liquidation preference may not be available to justify a difference in the valuation of the shares issued to investors and the valuation of contemporaneous shares or options issued to employees, although UK companies sometimes attempt to use dual ordinary class structures e. This is a problem that simply needs to be managed — there is no clear solution to this if the UK company wishes to issue SEIS or EIS qualifying shares to investors and make contemporaneous grants to US employees.
Take into account the local taxation of share and option grants. You will need advice in each jurisdiction in which you make equity grants as to what mechanisms work best.
- option trading in kannada.
- Comparison of UK and US share incentive arrangements | Legal Guidance | LexisNexis!
- Incentive Stock Options Checklist | Practical Law.
- iq binary option withdrawal.
- wrd stock options!
- Making UK Equity Plans Work for US Employees. - Marks Paneth!
- binary options nadex demo;
In the US, as suggested above, a share grant that is taxed as ordinary income at fair market value at the time of grant with no discount for risk of forfeiture due to reverse vesting may make sense for some senior executives if the current valuation of your shares is low enough; otherwise, you will need to grant options. Specifically, in order to benefit from tax-favoured treatment, the ISO needs to be exercised and the shares so obtained need to be held for at least one year prior to disposition.
This is an unlikely scenario for most employees, particularly in the context of a trade sale exit.
- forex gain formula system.
- Frequently asked questions about stock options and tax implications!
- liteforex mt4 android.
- elliott wave course forex.
- cara scalping dalam forex!
- Do you want to find out more about Croner-i?.
- tips trading forex dengan modal kecil;
The value of these options above their exercise price is taxed at ordinary income rates at the time of exercise which in most instances is likely to be at the time of exit , but this would also be the case for an ISO if it is only exercised at the time of exit. With an NQSO, the value of the shares so issued over the option exercise price is deductible by the company as a compensation expense — the company can, if it wishes, choose to share the benefit of this with the employee.
Tax advantaged share plans—UK and US comparison
Talk to a tax professional to learn how to plan for your AMT liability. In order to take advantage of the ISO tax benefit, you need to meet certain holding periods. Specifically, you must hold keep ISOs for at least one year after exercising and two years after your options were granted. If either of these holdings periods is not met for example, if you participate in a tender offer and decide to exercise and sell in one transaction , the difference between your strike price and the sale price of shares will be taxed as ordinary income.
This applies even if your company gives you more than 90 days to exercise after leaving. As discussed in Part 1 , most companies require you to exercise your vested stock options within a set window of time after leaving the company. This window, called a post-termination exercise PTE period , is usually around 90 days. As you can see in the graph above, the benefit of doing this is that you are minimizing the pre-exercise gain. This could potentially limit your exposure to AMT.
The downside here that you are taking on risk. There is no guarantee that your stock will ever be liquid, so you are paying to buy stock that could one day be worthless. If you choose to exercise options early, you must file an 83 b election to take advantage of the beneficial tax treatment.
Equity How stock options are taxed | Carta
You only have 30 days to file this with the IRS, and there are no exceptions. The third common time to exercise your stock options is upon an exit, such as an IPO or acquisition. This is the least risky time to exercise because you know the stock is liquid. You can turn around and sell the stock for a gain hopefully the same day you pay to buy it.
The downside in this situation is that you usually end up paying more taxes. Remember: If you want to qualify for favorable tax treatment, you need to hold your ISOs for at least one year after exercising. If this happens, your options will be treated like NSOs, and any spread between your strike price and the stock price when you exercise is taxed as ordinary income. Equity part 1 : Startup employee stock options.
Comparison of UK and US share incentive arrangements
Equity part 2 : Stock option strike prices. Carta employee resource center. How to value your equity offer free startup equity calculator. Employee Shareholder Bill of Rights.