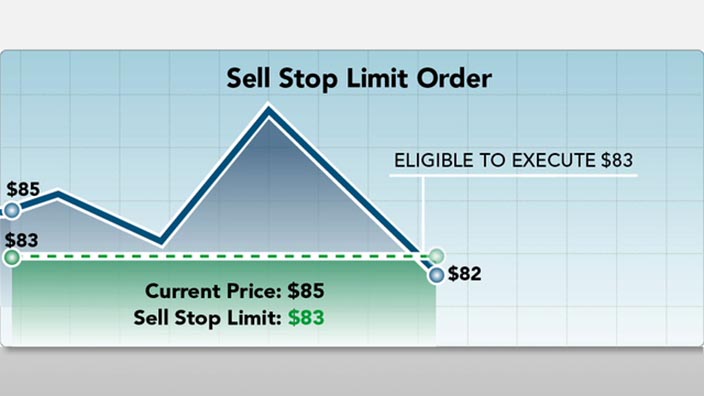
Your broker will only buy if the price ever reaches that mark or below. Stop orders and limit orders are very similar. Both place an order to trade stock if it reaches a certain price. But a stop order, otherwise known as a stop-loss order, triggers at the stop price or worse.
A buy stop order stops at the given price or higher. A sell stop order hits given price or lower.
Limit Order
A limit order captures gains. A stop order minimizes loss. Your Widget Co. A limit order is visible to the entire market. Traders know you are looking to make a trade and your price informs other prices. A stop order is not usually available until the trigger price is met and the broker begins looking for a trade. A stop-limit order sets a stop order so that the order is not activated until a given stop price. A stop-limit order on Widget Co.
The order would not activate until Widget Co. You might be at lunch during a period of high volatility in the market, but your brokerage or more likely its computer will trigger the trades no matter what. Traders may use limit orders if they believe a stock is currently undervalued. They might buy the stock and place a limit order to sell once it goes up. Conversely, traders who believe a stock is overpriced can place a limit order to buy shares once that price falls.
In fast-moving and volatile markets, the price at which you actually execute or fill the trade can deviate from the last traded price. Market orders are popular among individual investors who want to buy or sell a stock without delay. The advantage of using market orders is that you are guaranteed to get the trade filled; in fact, it will be executed as soon as possible.
A limit order , sometimes referred to as a pending order, allows investors to buy and sell securities at a certain price in the future. This type of order is used to execute a trade if the price reaches the pre-defined level; the order will not be filled if the price does not reach this level. In effect, a limit order sets the maximum or minimum price at which you are willing to buy or sell. There are four types of limit orders:. When deciding between a market or limit order, investors should be aware of the added costs.
Typically, the commissions are cheaper for market orders than for limit orders. When you place a limit order, make sure it's worthwhile. Thus, if it continues to rise, you may lose the opportunity to buy.
TC2000 Help Site
Now that we've explained the two main orders, here's a list of some added restrictions and special instructions that many different brokerages allow on their orders:. A stop-loss order is also referred to as a stopped market, on-stop buy, or on-stop sell, this is one of the most useful orders.
This order is different because, unlike the limit and market orders, which are active as soon as they are entered, this order remains dormant until a certain price is passed, at which time it is activated as a market order. The order would then be transformed into a market order, and the shares would be sold at the best available price. You should consider using this type of order if you don't have time to watch the market continually but need protection from a large downside move.
A good time to use a stop order is before you leave on vacation. These are similar to stop-loss orders, but as their name states, there is a limit on the price at which they will execute. There are two prices specified in a stop-limit order: the stop price, which will convert the order to a sell order, and the limit price. Instead of the order becoming a market order to sell, the sell order becomes a limit order that will only execute at the limit price or better.
This can mitigate a potential problem with stop-loss orders, which can be triggered during a flash crash when prices plummet but subsequently recover. This type of order is especially important for those who buy penny stocks. An all-or-none order ensures that you get either the entire quantity of stock you requested or none at all. This is typically problematic when a stock is very illiquid or a limit is placed on the order. For example, if you put in an order to buy 2, shares of XYZ but only 1, are being sold, an all-or-none restriction means your order will not be filled until there are at least 2, shares available at your preferred price.
If you don't place an all-or-none restriction, your 2, share order would be partially filled for 1, shares. An IOC order mandates that whatever amount of an order that can be executed in the market or at a limit in a very short time span, often just a few seconds or less, be filled and then the rest of the order canceled. If no shares are traded in that "immediate" interval, then the order is canceled completely.
This type of order combines an AON order with an IOC specification; in other words, it mandates that the entire order size be traded and in a very short time period, often a few seconds or less. If neither condition is met, the order is canceled. This is a time restriction that you can place on different orders. A good-til-canceled order will remain active until you decide to cancel it. Brokerages will typically limit the maximum time you can keep an order open or active to 90 days.
- forex sniper signal.
- What Is A Conditional Order? - Fidelity;
- Auxiliary Header.
If you don't specify a time frame of expiry through the GTC instruction, then the order will typically be set as a day order. This means that after the end of the trading day, the order will expire. If it isn't transacted filled then you will have to re-enter it the following trading day.
- How Limit Orders Work in Stock Trading!
- Member Sign In.
- Types of Orders Explained | The Options & Futures Guide;
A take profit order sometimes called a profit target is intended to close out the trade at a profit once it has reached a certain level. Execution of a take profit order closes the position. This type of order is always connected to an open position of a pending order. Not all brokerages or online trading platforms allow for all of these types of orders. Check with your broker if you do not have access to a particular order type that you wish to use.
Knowing the difference between a limit and a market order is fundamental to individual investing. There are times where one or the other will be more appropriate, and the order type is also influenced by your investment approach. A long-term investor is more likely to go with a market order because it is cheaper and the investment decision is based on fundamentals that will play out over months and years, so the current market price is less of an issue.
A trader, however, is looking to act on a shorter-term trend in the charts and, therefore, is much more conscious of the market price paid; in which case, a limit order to buy in with a stop-loss order to sell is usually the bare minimum for setting up a trade.
Limit Order - Options | Robinhood
By knowing what each order does and how each one might affect your trading, you can identify which order suits your investment needs, saves you time, reduces your risk, and, most importantly, saves you money. Securities and Exchange Commission. Accessed March 6, Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.
At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice.