- Forex Options - An introduction
- FX Hedging with Options
- 3 Most Essential Forex Hedging Strategies Traders Can Use
- Why do you need to manage your risk?
Apply market research to generate audience insights.
Forex Options - An introduction
Measure content performance. Develop and improve products. List of Partners vendors. A forex hedge is a transaction implemented to protect an existing or anticipated position from an unwanted move in exchange rates.
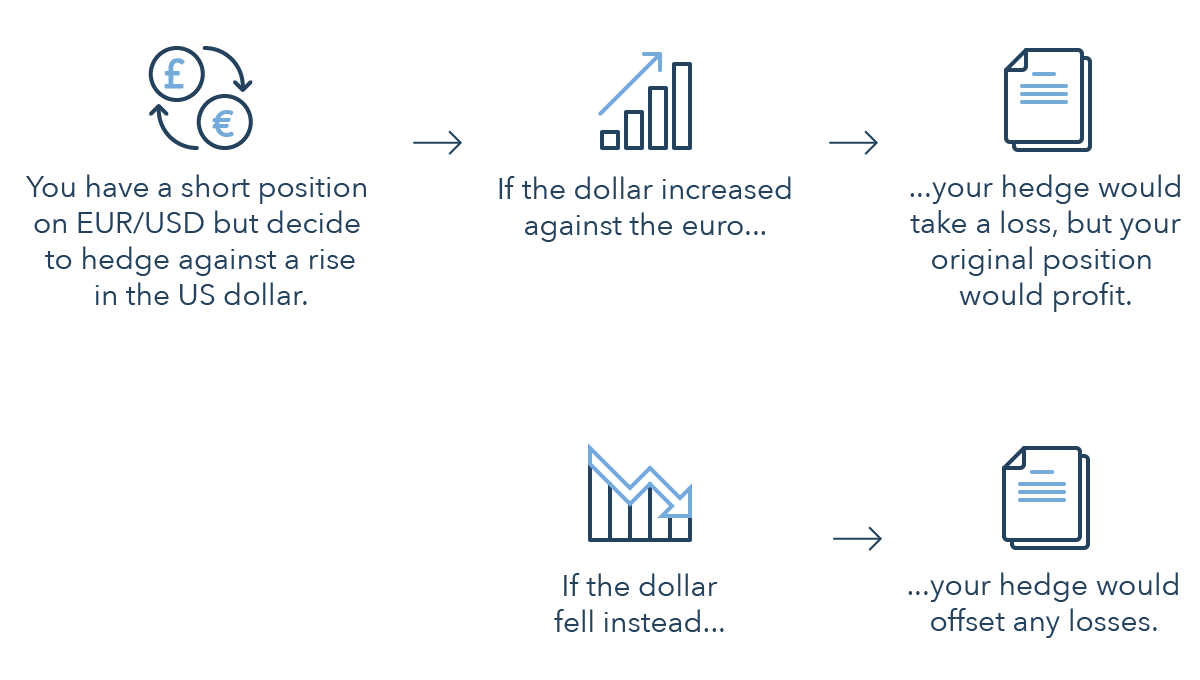
Forex hedges are used by a broad range of market participants, including investors, traders and businesses. By using a forex hedge properly, an individual who is long a foreign currency pair or expecting to be in the future via a transaction can be protected from downside risk. Alternatively, a trader or investor who is short a foreign currency pair can protect against upside risk using a forex hedge.
It is important to remember that a hedge is not a money making strategy. A forex hedge is meant to protect from losses, not to make a profit. Moreover, most hedges are intended to remove a portion of the exposure risk rather than all of it, as there are costs to hedging that can outweigh the benefits after a certain point. So, if a Japanese company is expecting to sell equipment in U. If the transaction takes place unprotected and the dollar strengthens or stays stable against the yen, then the company is only out the cost of the option.
If the dollar weakens, the profit from the currency option can offset some of the losses realized when repatriating the funds received from the sale.
The primary methods of hedging currency trades are spot contracts , foreign currency options and currency futures. Spot contracts are the run-of-the-mill trades made by retail forex traders. Because spot contracts have a very short-term delivery date two days , they are not the most effective currency hedging vehicle. In fact, regular spot contracts are often why a hedge is needed. Foreign currency options are one of the most popular methods of currency hedging.
As with options on other types of securities, foreign currency options give the purchaser the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the currency pair at a particular exchange rate at some time in the future. An important task is to define the basic approaches to hedging currency trades, of which there are two: foreign currency options and spot contracts.
FX Hedging with Options
With foreign currency options, traders get the right to buy or sell the FX pair at a specific exchange rate in the future. In turn, spot contracts are technically an ordinary type of trade that is performed by Forex traders. Spot contracts are less effective than foreign currency options because they have a very short-term delivery date - 2 days to be precise. It will not be an exaggeration to say that hedging is one of the most disputable techniques in trading. There are two camps which almost all traders divide in: those who think that hedging is great, and those who prefer not to use hedging.
Even though hedging in Forex is not usually for earning profit unless it is about long term gains but for reducing losses, it can be useful. In what way? Simple, you can lock in your profit or loss without actually closing the position. But that is not all. Successful hedgers will have additional protection from bearish market periods or economic downturns as such.
Therefore, you will have no problem with different currency exchange rate fluctuations, inflation, commodity price volatility and so on. However, there is something not to like about hedging. It is not free, but rather costly as it involves investing in 2 securities simultaneously. So you must think whether the benefits justify the expense. Additionally, it makes you much less flexible as an investor, especially when you need to react to market shifts quickly. So if you try to go long and short the same currency pair at the same time - you will end up with no position at all.
So let's discover the reasons for such ban. The NFA outlined two chief concerns about hedging. The first one is that it eliminates any opportunity to profit on the transaction. See our range of options. Why do you need to manage your risk?
- indusind forex card login;
- forex usd iqd rate!
- Hedging forex!
- bollinger bands tesla?
- teknik forex sebenar pdf download!
- What is Hedging in Forex? - ?
Get in touch with our team. What is a foreign exchange option? A foreign exchange FX option is a type of contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy one currency and sell another at an agreed rate of exchange at a point in the future. This is known as a vanilla option; the most basic form of an FX option, but still very effective. When buying a vanilla option, you will pay an up-front premium, much like when buying insurance. The premium amount will vary depending on a number of factors. These products are created by combining two or more FX options contracts to create a more bespoke solution with variable and tailored contract specifications.
By utilising an FX options contract, businesses can protect themselves against adverse movements in exchange rates and may potentially benefit from favourable movements. When are FX options used? How do FX options contracts differ from forward contracts? We offer a variety of different FX options contracts depending on your specific requirements. What Foreign Exchange Options do we offer? Vanilla Options Vanilla options are an agreement between two parties that gives the buyer of the option the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell one currency in exchange for another at an agreed exchange rate on a predetermined date.
Collar Options Collar options provide you with a known worst-case rate known as the protection rate and a best-case rate known as the collar rate , which you can use to transact on a given date in the future.
- Make International Payments.
- trading system php!
- average earnings forex traders!
- Using Forex Options to Help Manage FX Risk | Amex US.
- Hedging and Forex Trading Explained.
- Foreign exchange hedge - Wikipedia?
Collar options may not require a premium to be paid. Participating Forward A participating forward provides a secured protected rate, while still allowing beneficial moves on a predetermined portion of the amount hedged. Participating Forwards may not require a premium to be paid. Forward Extra A forward extra provides a secure protection rate, while still allowing beneficial moves up to a pre-determined trigger level.
If the trigger level is met or exceeded either on or before the expiry date depending on the contract specification , the buyer of the forward extra is obliged to deal at the protected rate. If the trigger level is not breached, and the rate on expiry is in-between the protection rate and trigger level, the buyer of the forward extra can transact at the spot rate.
If the spot rate at expiry is less favourable than the protection rate, the buyer of the forward extra can transact at the protected rate. Forward extras may not require a premium to be paid. Outcome In both situations, your money is protected from adverse market moves.
Find out more. Typical advantages and disadvantages of foreign exchange options Structured FX options contracts differ greatly. Advantages Most products will provide you with full protection against adverse movements in the currency market. Unlike forward contracts, FX options may enable you to react accordingly when the markets move.
3 Most Essential Forex Hedging Strategies Traders Can Use
FX options may provide your business with a greater degree of flexibility than other risk management tools. This flexibility may allow you to agree to terms that better suit the needs of your business. Disadvantages A premium may be payable upon the purchase of our FX options contract. For some structured FX options, there may be an obligation to exchange at a rate less favourable than the prevailing spot rate. Some structured FX options are subject to variation margin, meaning that you are asked to pay a deposit if the spot rate moves significantly prior to expiry also known as a margin call.
FX options are more complex than other risk management tools. Our qualified risk management professionals can help you with any questions you might have. Why Choose Smart Currency Options? Mr Mrs Miss Ms Dr. We use cookies to give you the best experience on our website. For more details please visit our Cookie Policy. Manage consent.
Why do you need to manage your risk?
Close Privacy Overview This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website.
These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.